In computer programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code. For example, if you want to show a message 100 times, then you can use a loop. It's just a simple example; you can achieve much more with loops.
In the previous tutorial, you learned about Java for loop. Here, you are going to learn about while and do...while loops.
Java while loop
Java while loop is used to run a specific code until a certain condition is met. The syntax of the while loop is:
while (testExpression) {
// body of loop
}
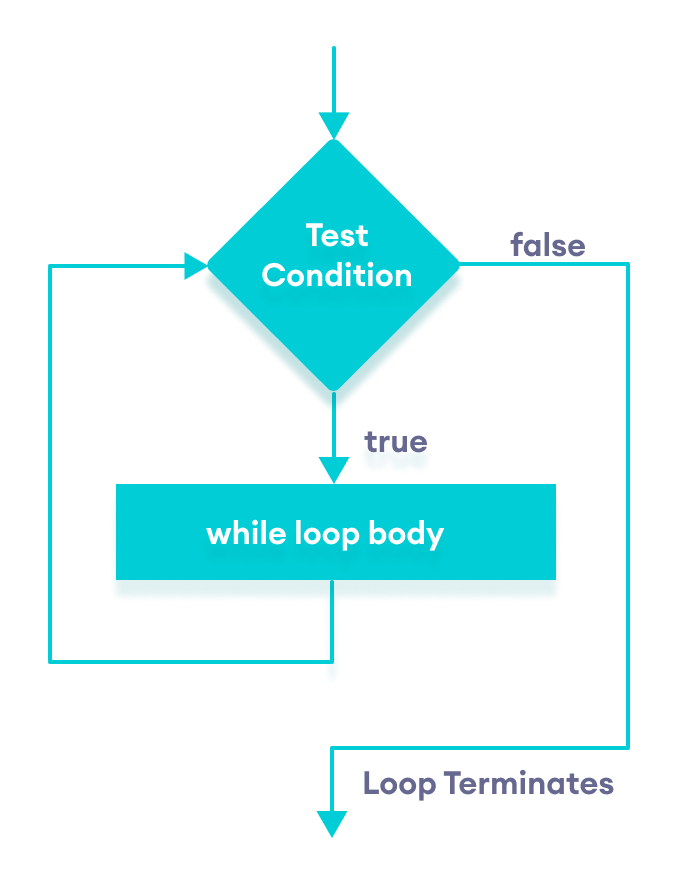
Here,
- A
whileloop evaluates the textExpression inside the parenthesis(). - If the textExpression evaluates to
true, the code inside thewhileloop is executed. - The textExpression is evaluated again.
- This process continues until the textExpression is
false. - When the textExpression evaluates to
false, the loop stops.
To learn more about the conditions, visit Java relational and logical operators.
Flowchart of while loop
Example 1: Display Numbers from 1 to 5
// Program to display numbers from 1 to 5
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declare variables
int i = 1, n = 5;
// while loop from 1 to 5
while(i <= n) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how this program works.
| Iteration | Variable | Condition: i | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1n = 5 |
true |
1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2n = 5 |
true |
2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3n = 5 |
true |
3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
| 4th | i = 4n = 5 |
true |
4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5n = 5 |
true |
5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6n = 5 |
false |
The loop is terminated |
Example 2: Sum of Positive Numbers Only
// Java program to find the sum of positive numbers
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
// create an object of Scanner class
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// take integer input from the user
System.out.println("Enter a number");
int number = input.nextInt();
// while loop continues
// until entered number is positive
while (number >= 0) {
// add only positive numbers
sum += number;
System.out.println("Enter a number");
number = input.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
input.close();
}
}
Output
Enter a number 25 Enter a number 9 Enter a number 5 Enter a number -3 Sum = 39
In the above program, we have used the Scanner class to take input from the user. Here, nextInt() takes integer input from the user.
The while loop continues until the user enters a negative number. During each iteration, the number entered by the user is added to the sum variable.
When the user enters a negative number, the loop terminates. Finally, the total sum is displayed.
Java do...while loop
The do...while loop is similar to while loop. However, the body of do...while loop is executed once before the test expression is checked. For example,
do {
// body of loop
} while(textExpression);
Here,
- The body of the loop is executed at first. Then the textExpression is evaluated.
- If the textExpression evaluates to
true, the body of the loop inside thedostatement is executed again. - The textExpression is evaluated once again.
- If the textExpression evaluates to
true, the body of the loop inside thedostatement is executed again. - This process continues until the textExpression evaluates to
false. Then the loop stops.
Flowchart of do...while loop
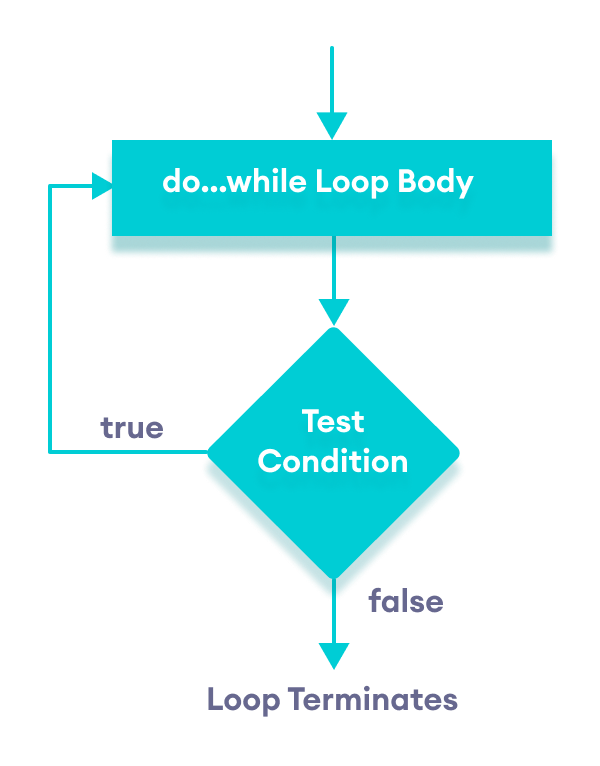
Let's see the working of do...while loop.
Example 3: Display Numbers from 1 to 5
// Java Program to display numbers from 1 to 5
import java.util.Scanner;
// Program to find the sum of natural numbers from 1 to 100.
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1, n = 5;
// do...while loop from 1 to 5
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while(i <= n);
}
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how this program works.
| Iteration | Variable | Condition: i | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
i = 1n = 5 |
not checked | 1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
|
| 1st | i = 2n = 5 |
true |
2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
| 2nd | i = 3n = 5 |
true |
3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
| 3rd | i = 4n = 5 |
true |
4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
| 4th | i = 5n = 5 |
true |
5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
| 5th | i = 6n = 5 |
false |
The loop is terminated |
Example 4: Sum of Positive Numbers
// Java program to find the sum of positive numbers
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int number = 0;
// create an object of Scanner class
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// do...while loop continues
// until entered number is positive
do {
// add only positive numbers
sum += number;
System.out.println("Enter a number");
number = input.nextInt();
} while(number >= 0);
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
input.close();
}
}
Output 1
Enter a number 25 Enter a number 9 Enter a number 5 Enter a number -3 Sum = 39
Here, the user enters a positive number, that number is added to the sum variable. And this process continues until the number is negative. When the number is negative, the loop terminates and displays the sum without adding the negative number.
Output 2
Enter a number -8 Sum is 0
Here, the user enters a negative number. The test condition will be false but the code inside of the loop executes once.
Infinite while loop
If the condition of a loop is always true, the loop runs for infinite times (until the memory is full). For example,
// infinite while loop
while(true){
// body of loop
}
Here is an example of an infinite do...while loop.
// infinite do...while loop
int count = 1;
do {
// body of loop
} while(count == 1)
In the above programs, the textExpression is always true. Hence, the loop body will run for infinite times.
for and while loops
The for loop is used when the number of iterations is known. For example,
for (let i = 1; i <=5; ++i) {
// body of loop
}
And while and do...while loops are generally used when the number of iterations is unknown. For example,
while (condition) {
// body of loop
}
Also Read:
