In computer programming, the if statement is a conditional statement. It is used to execute a block of code only when a specific condition is met. For example,
Suppose we need to assign different grades to students based on their scores.
- If a student scores above 90, assign grade A
- If a student scores above 75, assign grade B
- If a student scores above 65, assign grade C
These conditional tasks can be achieved using the if statement.
Python if Statement
An if statement executes a block of code only if the specified condition is met.
Syntax
if condition:
# body of if statement
Here, condition is a boolean expression, such as number >5, that evaluates to either True or False.
- If
conditionevaluates toTrue, the body of theifstatement is executed. - If
conditionevaluates toFalse, the body of theifstatement will be skipped from execution.
Let's look at an example.
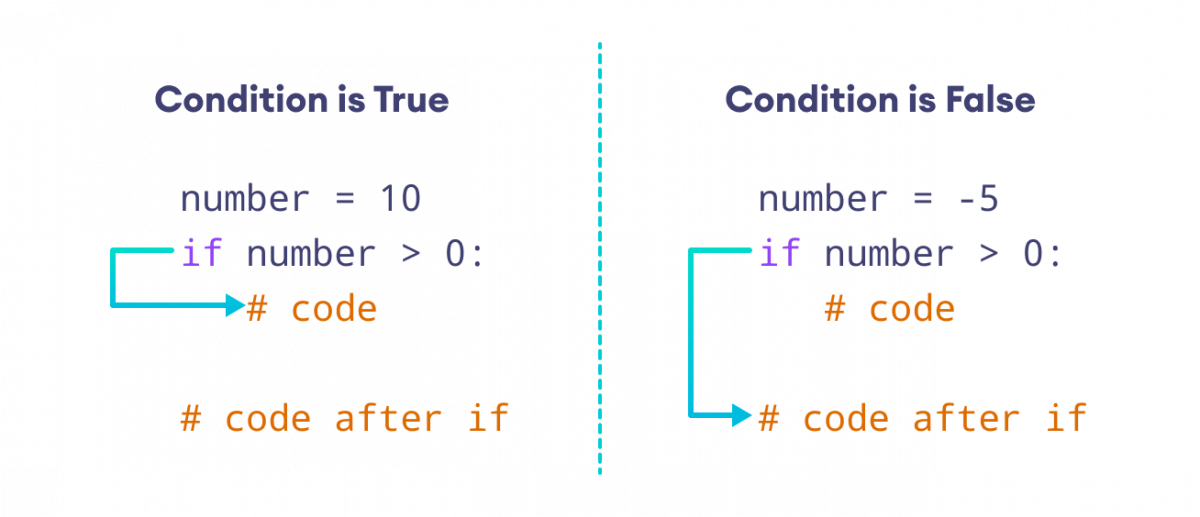
Example: Python if Statement
number = int(input('Enter a number: '))
# check if number is greater than 0
if number > 0:
print(f'{number} is a positive number.')
print('A statement outside the if statement.')
Sample Output 1
Enter a number: 10 10 is a positive number. A statement outside the if statement.
If user enters 10, the condition number > 0 evalutes to True. Therefore, the body of if is executed.
Sample Output 2
Enter a number: -2 A statement outside the if statement.
If user enters -2, the condition number > 0 evalutes to False. Therefore, the body of if is skipped from execution.
Indentation in Python
Python uses indentation to define a block of code, such as the body of an if statement. For example,
x = 1
total = 0
# start of the if statement
if x != 0:
total += x
print(total)
# end of the if statement
print("This is always executed.")
Here, the body of if has two statements. These statements execute only if x != 0 evaluate to True.
You will get an error if you write the above code like this:
# Error code
x = 1
total = 0
if x != 0:
total += x
print(total)
Here, we haven't used indentation after the if statement. In this case, Python thinks our if statement is empty, which results in an error.
Python if...else Statement
An if statement can have an optional else clause. The else statement executes if the condition in the if statement evaluates to False.
Syntax
if condition:
# body of if statement
else:
# body of else statement
Here, if the condition inside the if statement evaluates to
- True - the body of
ifexecutes, and the body ofelseis skipped. - False - the body of
elseexecutes, and the body ofifis skipped
Let's look at an example.
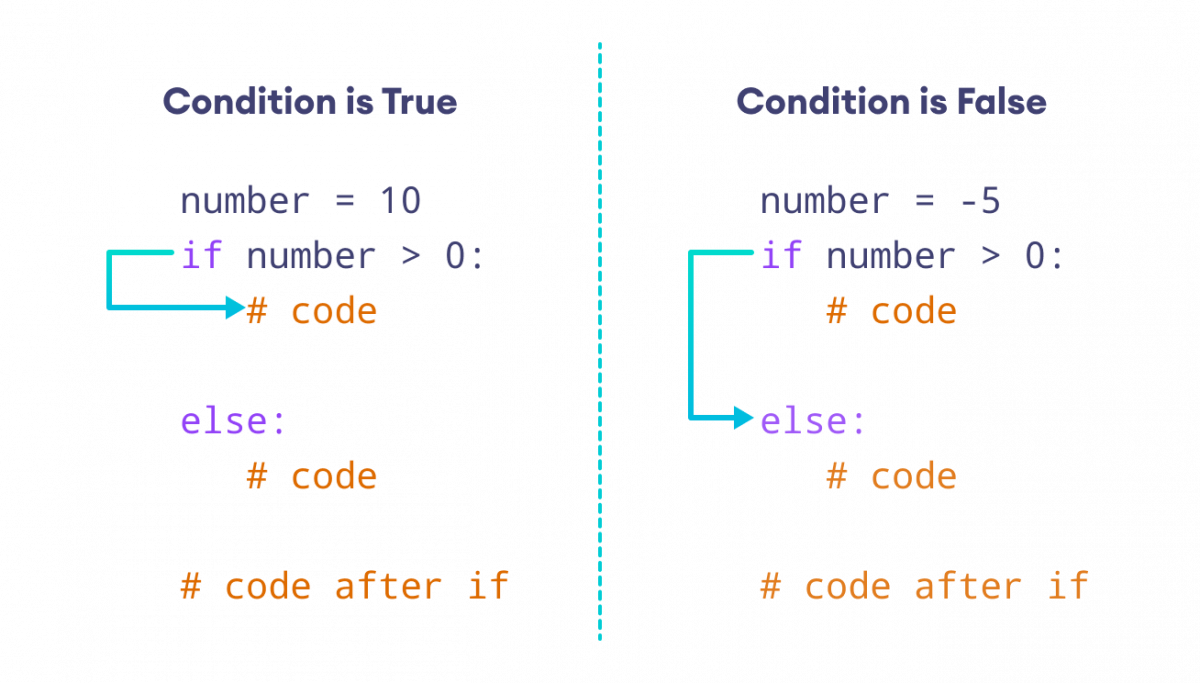
Example: Python if…else Statement
number = int(input('Enter a number: '))
if number > 0:
print('Positive number')
else:
print('Not a positive number')
print('This statement always executes')
Sample Output 1
Enter a number: 10 Positive number This statement always executes
If user enters 10, the condition number > 0 evalutes to True. Therefore, the body of if is executed and the body of else is skipped.
Sample Output 2
Enter a number: 0 Not a positive number This statement always executes
If user enters 0, the condition number > 0 evalutes to False. Therefore, the body of if is skipped and the body of else is executed.
Python if…elif…else Statement
The if...else statement is used to execute a block of code among two alternatives.
However, if we need to make a choice between more than two alternatives, we use the if...elif...else statement.
Syntax
if condition1:
# code block 1
elif condition2:
# code block 2
else:
# code block 3
Let's look at an example.
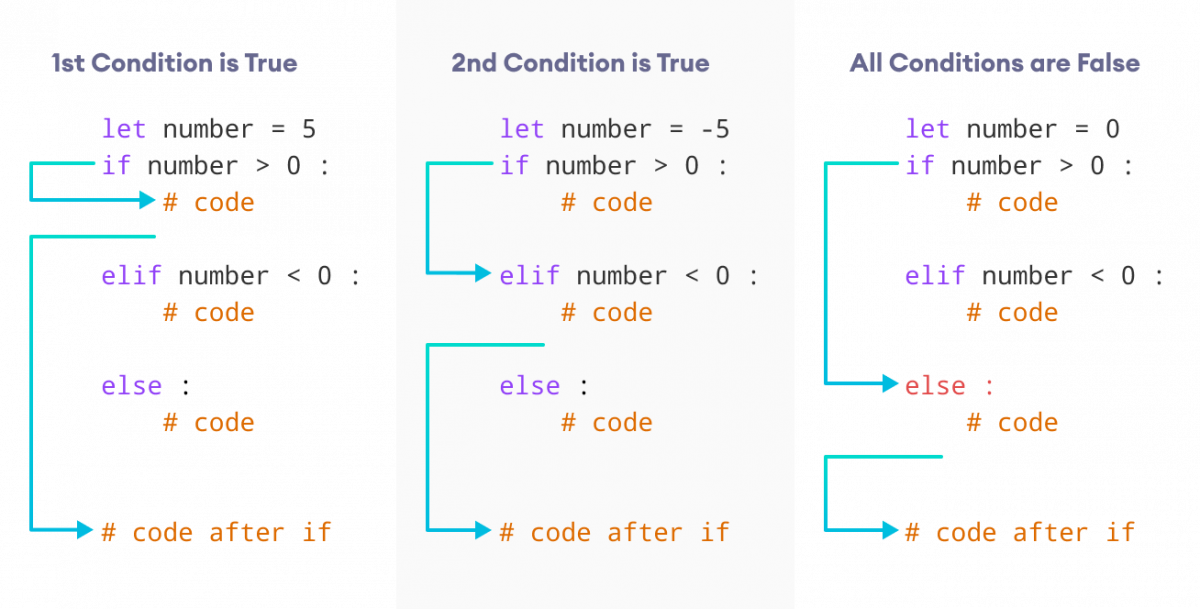
Example: Python if…elif…else Statement
number = -5
if number > 0:
print('Positive number')
elif number < 0:
print('Negative number')
else:
print('Zero')
print('This statement is always executed')
Output
Negative number This statement is always executed
Here, the first condition, number > 0 evaluates to False. In this scenario, the second condition is checked.
The second condition, number < 0 evaluates to True. Therefore, the statements inside the elif block is executed.
In the above program, it is important to note that regardless the value of number variable, only one block of code will be executed.
Python Nested if Statements
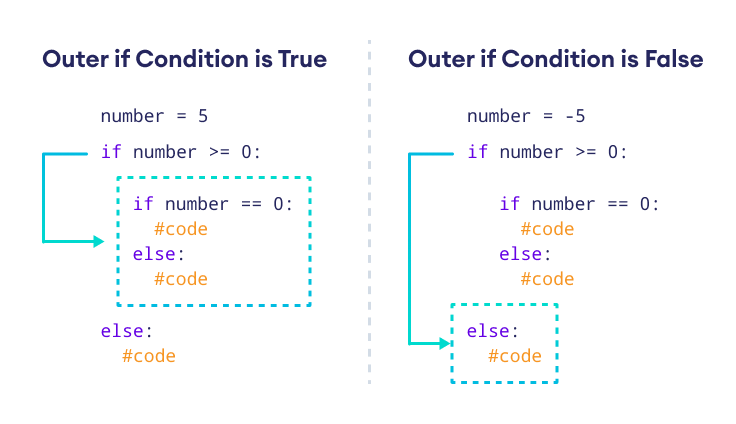
It is possible to include an if statement inside another if statement. For example,
number = 5
# outer if statement
if number >= 0:
# inner if statement
if number == 0:
print('Number is 0')
# inner else statement
else:
print('Number is positive')
# outer else statement
else:
print('Number is negative')
Output
Number is positive
Here's how this program works.
More on Python if…else Statement
if Statement
In certain situations, the if statement can be simplified into a single line. For example,
number = 10
if number > 0:
print('Positive')
This code can be compactly written as
number = 10
if number >0: print('Positive')
This one-liner approach retains the same functionality but in a more concise format.
if...else
Python doesn't have a ternary operator. However, we can use if...else to work like a ternary operator in other languages. For example,
grade = 40
if grade >= 50:
result = 'pass'
else:
result = 'fail'
print(result)
can be written as
grade = 40
result = 'pass' if number >= 50 else 'fail'
print(result)
We can use logical operators such as and and or within an if statement.
age = 35
salary = 6000
# add two conditions using and operator
if age >= 30 and salary >= 5000:
print('Eligible for the premium membership.')
else:
print('Not eligible for the premium membership')
Output
Eligible for the premium membership.
Here, we used the logical operator and to add two conditions in the if statement.
We also used >= (comparison operator) to compare two values.
Logical and comparison operators are often used with if...else statements. Visit Python Operators to learn more.
