In programming, the break and continue statements are used to alter the flow of loops:
breakexits the loop entirelycontinueskips the current iteration and proceeds to the next one
Python break Statement
The break statement terminates the loop immediately when it's encountered.
Syntax
break
Working of Python break Statement
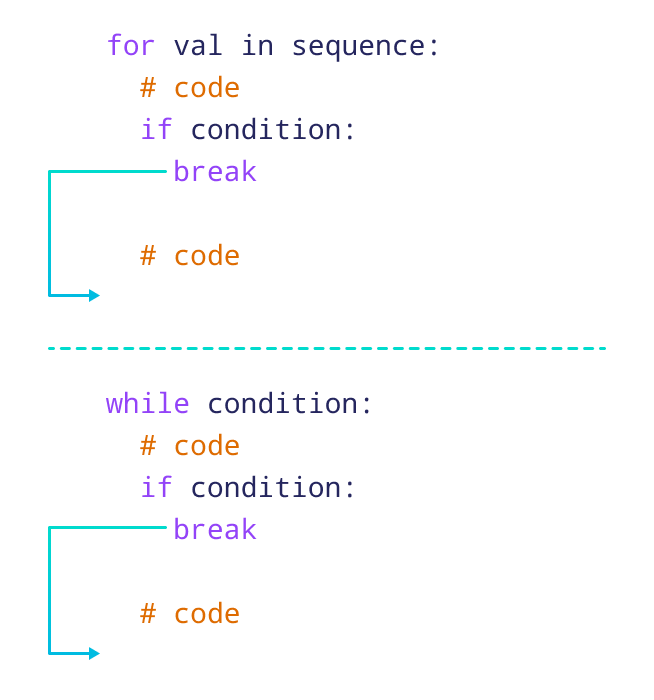
The above image shows the working of break statements in for and while loops.
Note: The break statement is usually used inside decision-making statements such as if...else.
Example: break Statement with for Loop
We can use the break statement with the for loop to terminate the loop when a certain condition is met. For example,
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
Output
0 1 2
In the above example,
if i == 3:
break
terminates the loop when i is equal to 3. Hence, the output doesn't include values after 2.
Note: We can also terminate the while loop using a break statement.
We can also terminate the while loop using the break statement. For example,
i = 0
while i < 5:
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
i += 1
Output
0 1 2
In the above example,
if i == 3:
break
terminates the loop when i is equal to 3.
Python continue Statement
The continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop and the control flow of the program goes to the next iteration.
Syntax
continue
Working of continue Statement in Python
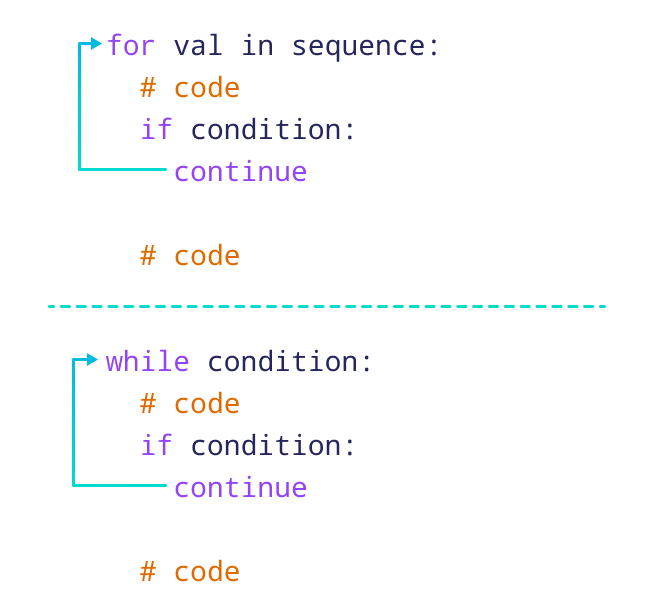
Example: continue Statement with for Loop
We can use the continue statement with the for loop to skip the current iteration of the loop and jump to the next iteration. For example,
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
Output
0 1 2 4
In the above example,
if i == 3:
continue
skips the current iteration when i is equal to 3, and continues the next iteration. Hence, the output has all the values except 3.
Note: We can also use the continue statement with a while loop.
We can skip the current iteration of the while loop using the continue statement. For example,
# Program to print odd numbers from 1 to 10
num = 0
while num < 10:
num += 1
if (num % 2) == 0:
continue
print(num)
Output
1 3 5 7 9
In the above example, we have used the while loop to print the odd numbers between 1 and 10. Here,
if (num % 2) == 0:
continue
skips the current iteration when the number is even and starts the next iteration.
Also Read:

